728x90
컬렉션 List의 메소드 중에서 매개변수에 넣는 것 파악하고
반환타입도 파악하면서
해당 반환 타입으로 뭘 할 수 있을지 고민하다가
int타입으로 반환되는 indexOf()를 if문과 연결지어 간단한 출력문구 사용
boolean으로 반환되는 isEmpty()나 remove() 등도 if문 조건으로 사용해봄
이외에도 get이나 다른 str이나 다른 타입 반환을 이용해서 ==이나 equals() 같은 걸 이용해서 값 비교해서
찾는 조건 같은걸로 while, for문 같은 것도 사용해봐야겠다
/******************************** collection 3rd practice ***************************************/
public void method03() {
// 3번째 연습할거는 오버라이딩 해제하면서, equals()와 hashCode() 비교
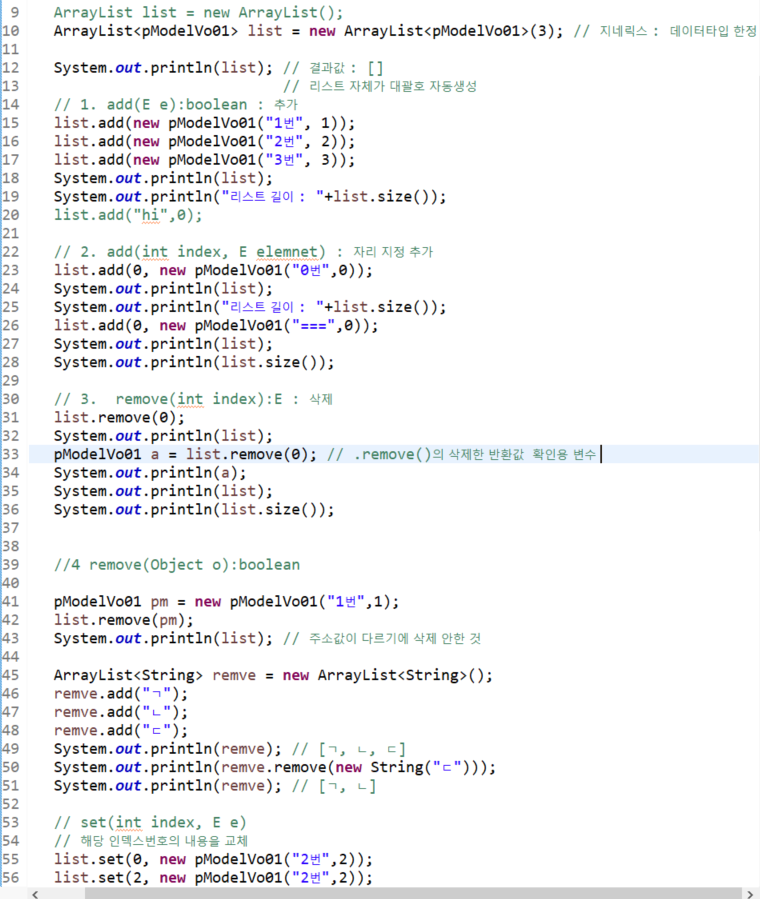
ArrayList a = new ArrayList(2); // 제네릭 안써서 노란줄 경고
ArrayList<Student> al = new ArrayList<Student>(2);
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>(1);
// vo클래스에 있는 오버라이딩된 toStirng(), equals(), hashCoding()
// 전부 주석처리
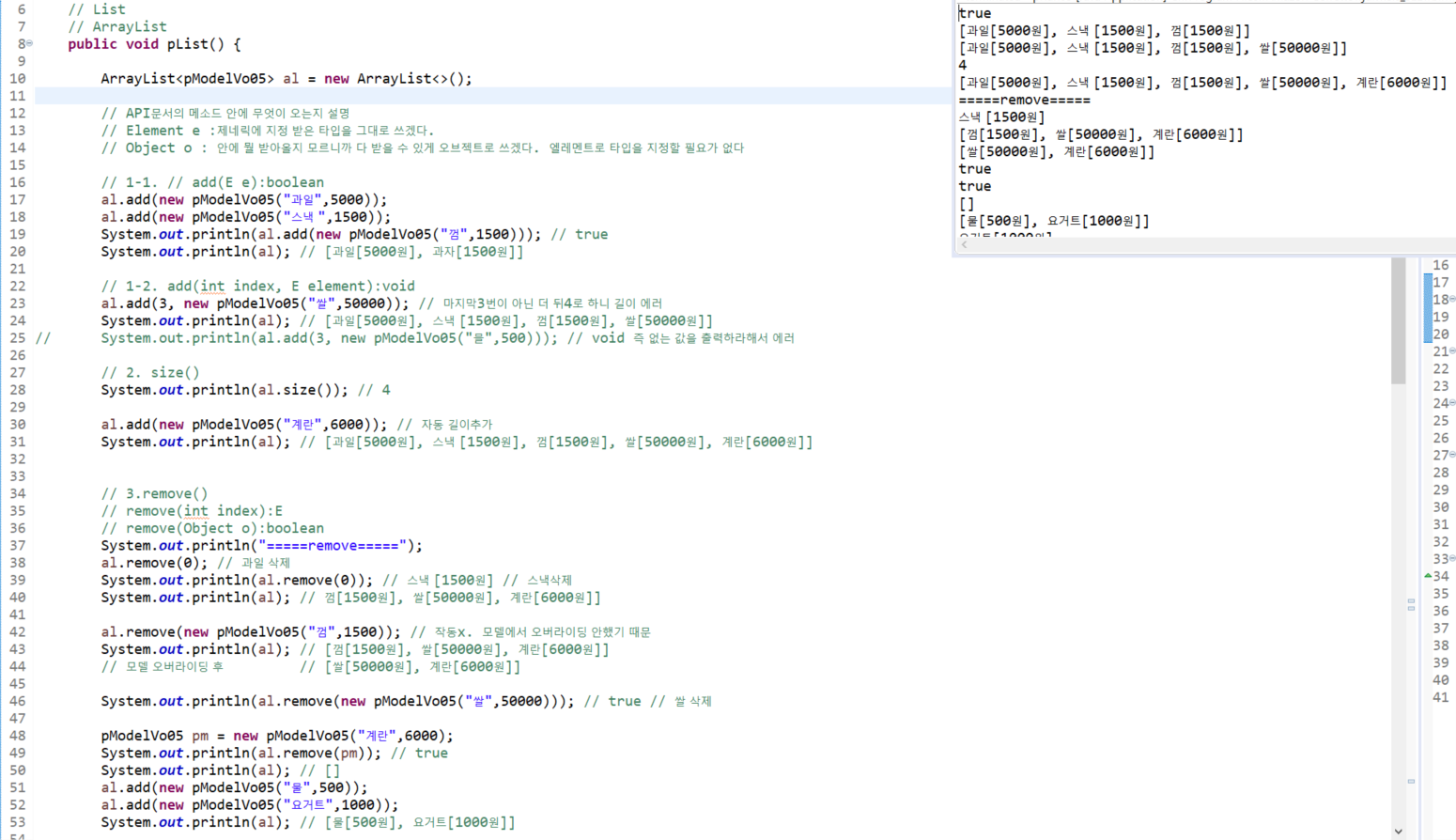
// add(E e):boolean
al.add(new Student("ㄱ",100));
al.add(new Student("ㄴ",90));
System.out.println(al); // [ㄱ(100점), ㄴ(90점)]
// Object의 toString()를 오버라이딩 때문에 주소값이 아닌 객체값이 바로나옴
// toString() 오버라이딩 안된 경우(오버라이딩 주석처리) 결과값 : [chap12_Collection.A_List.model.vo.Student@6d06d69c, chap12_Collection.A_List.model.vo.Student@7852e922]
al.add(2, new Student("ㄷ",95));
System.out.println(al); // [chap12_Collection.A_List.model.vo.Student@6d06d69c, chap12_Collection.A_List.model.vo.Student@7852e922, chap12_Collection.A_List.model.vo.Student@4e25154f]
System.out.println(al); // toString오버라이딩 후 : [ㄱ(100점), ㄴ(90점), ㄷ(95점)]
// add(int index, E element)
list.add(0, new Student("ㄱㄱ",100));
System.out.println(list); // [ㄱㄱ(100점)]
list.add(1, new Student("ㄴㄴ",90));
list.add(2, new Student("ㄷㄷ",85));
System.out.println(list);// [ㄱㄱ(100점), ㄴㄴ(90점), ㄷㄷ(85점)]
// addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) : boolean
al.addAll(al);
System.out.println(al);// [ㄱ(100점), ㄴ(90점), ㄷ(95점), ㄱ(100점), ㄴ(90점), ㄷ(95점)]
// addAll(int index, Collection c) : boolean
al.addAll(1,al);
System.out.println(al); // [ㄱ(100점), ㄱ(100점), ㄴ(90점), ㄷ(95점), ㄱ(100점), ㄴ(90점), ㄷ(95점), ㄴ(90점), ㄷ(95점), ㄱ(100점), ㄴ(90점), ㄷ(95점)]
// toString() 오버라이딩 주석 후 : [chap12_Collection.A_List.model.vo.Student@6d06d69c, chap12_Collection.A_List.model.vo.Student@6d06d69c, chap12_Collection.A_List.model.vo.Student@7852e922, chap12_Collection.A_List.model.vo.Student@4e25154f, chap12_Collection.A_List.model.vo.Student@6d06d69c, chap12_Collection.A_List.model.vo.Student@7852e922, chap12_Collection.A_List.model.vo.Student@4e25154f, chap12_Collection.A_List.model.vo.Student@7852e922, chap12_Collection.A_List.model.vo.Student@4e25154f, chap12_Collection.A_List.model.vo.Student@6d06d69c, chap12_Collection.A_List.model.vo.Student@7852e922, chap12_Collection.A_List.model.vo.Student@4e25154f]
// 장점1. 크기 제약 x
// .size() : 인덱스 길이 반환
System.out.println(al.size()); // 12
// 장점2. 추가/삭제/정렬 기능처리 간단
// 삭제
// remove(int index):E
// // remove()의 return은 삭제한 값을 돌려준다
// list.remove(7);
list.remove(2);
System.out.println("remove(int index) : "+list); // [ㄱㄱ(100점), ㄴㄴ(90점)]
System.out.println(list.remove(1)); // ㄴㄴ(90점) <- 대괄호 없고, 지운 객체 반환(pop개념)
System.out.println(list); // [ㄱㄱ(100점)]
Student delList = al.remove(11);
System.out.println("delList : "+delList); // delList : ㄷ(95점)
System.out.println(al); // [ㄱ(100점), ㄱ(100점), ㄴ(90점), ㄷ(95점), ㄱ(100점), ㄴ(90점), ㄷ(95점), ㄴ(90점), ㄷ(95점), ㄱ(100점), ㄴ(90점)]
Student delList2 = al.remove(10);
System.out.println(delList2); // ㄴ(90점)
System.out.println(al); // [ㄱ(100점), ㄱ(100점), ㄴ(90점), ㄷ(95점), ㄱ(100점), ㄴ(90점), ㄷ(95점), ㄴ(90점), ㄷ(95점), ㄱ(100점)]
// 삭제
// remove(Object o):boolean
// 같은 데이터라면 앞에 있는거부터 삭제
al.remove(new Student("ㄷ",95));
al.remove(new Student("ㄷ",95));
System.out.println(al.remove(new Student("ㄷ",95))); // false
System.out.println(al); // [ㄱ(100점), ㄱ(100점), ㄴ(90점), ㄷ(95점), ㄱ(100점), ㄴ(90점), ㄷ(95점), ㄴ(90점), ㄷ(95점), ㄱ(100점), ㄴ(90점), ㄷ(95점)]
// equals()가 오버라이딩이 안되어 있어서 값 비교가 아니라 주소값 비교라 삭제 못한 것.
System.out.println(al.size());
// 지네릭 추가 : <String>
// equals랑 hashCode가 잘 오버라이딩이 되어있기 때문에 삭제 가능
ArrayList<String> sList = new ArrayList<>(2);
sList.add(new String("a"));
sList.add(1, new String("b"));
System.out.println(sList); // [a, b]
// 제네릭<String> 같은 경우, toString()이 오버라이딩 안되어있거나 데이터 리턴이 없어도 객체값을 잘 내보내줌
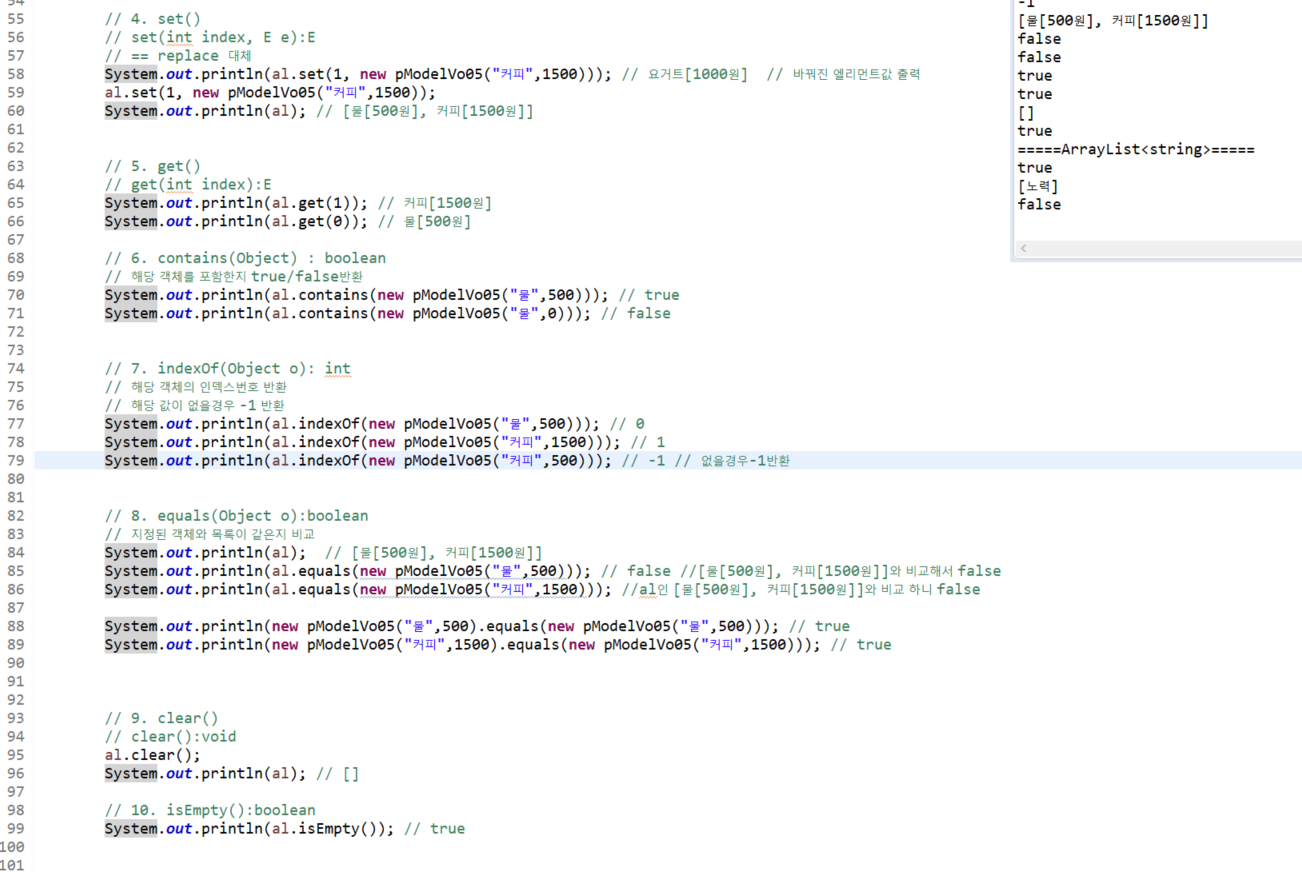
// set(int index, E e)
// 해당 인덱스 번호에 값 교체
sList.set(1, new String("changed Capital B"));
System.out.println(sList); // [a, changed Capital B]
al.set(0, new Student("a",50));
System.out.println(al); // [a(50점), ㄱ(100점), ㄴ(90점), ㄷ(95점), ㄱ(100점), ㄴ(90점), ㄷ(95점), ㄴ(90점), ㄷ(95점), ㄱ(100점), ㄴ(90점), ㄷ(95점)]
// get(int index):E
// 인덱스번호의 엘리먼트 값을 가져온다
sList.get(0);
String str = sList.get(1);
System.out.println(sList); // [a, changed Capital B]
System.out.println(str); // changed Capital B
// contains(Object) : boolean
// indexObject : int
System.out.println(al.contains(new Student("a",50))); // false
// int값 데이터 반환된 걸 if문에 적용
if(al.contains(new Student("ㄱ",100))){
System.out.println("포함 & 출력");
}else {
System.out.println("미포함. 값이 맞다면 equals()오버라이딩 체크해보세여");
} // equals()가 오버라이딩 되어있다면 값을 비교하기 때문에 contains()가 작동하고,
// 아닐 경우 값이 같더라도 주소값이 비교되기 때문에 작동x
al.indexOf(new Student("ㄴ",90));
System.out.println(al.indexOf(new Student("ㄴ",90))); // 2
// 반환된 인덱스번호로 if조건문 줘서 실행하기
if(al.indexOf(new Student("ㄴ",90)) > 0) {
al.remove(6);
System.out.println("indexOf의 번호가 0이상이면 객체값 하나 삭제함"); // indexOf의 번호가 0이상이면 객체값 하나 삭제함
}else {
System.out.println("조건 미충족. do nothing");
}
System.out.println(sList.get(0)); // a
// if((sList.get(0)) == "a") {
if((sList.get(0)).equals("a")) {
System.out.println("true"); // true
}else {
System.out.println("false");
}
// 반환된 boolean타입으로 while조건 사용하기
System.out.println("a : "+sList.contains("a")); // true
int i = 0;
while(sList.contains("a")) {
System.out.print(i+" "); // 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
i++;
if(i>=10) {
break; // while문 무한루프 + break문 사용
}
}
// while(true) {
// System.out.println("====");
// i++;
// if(i>=10) {
// break;
// }
// }
// while(sList.contains("a")) {
// if(i>=10) {
// break;
// }
// i += 2;
// System.out.print(i+ " ");
// }
// 지네릭<String>과 일반 참조객체<Student>의 오버라이딩 비교
// equals메소드와 해쉬코드가 오버라이딩 되지 않으면 주소값이 달라 없는걸로 나옴. 현재는 오버라이딩된 상태
// clear():void
al.clear();
System.out.println(al);// []
// isEmpty():boolean
al.isEmpty();
System.out.println(al.isEmpty()); // true
if(al.isEmpty()) {
al.add(new Student("new",10));
System.out.println(al); // [new(10점)]
}
}728x90
반응형
'small steps > 1일 1코딩 - 코딩을 내 몸처럼' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [1일1코딩][Java] 객체배열 practice 5th : 선언,할당,초기화, toString() (0) | 2022.08.18 |
|---|---|
| [1일1코딩][Java] 컬렉션 List 4th - equals(),toString() 추가제거 비교 (0) | 2022.08.16 |
| [1일1코딩][Java] 컬렉션 List 2nd (0) | 2022.08.14 |
| [1일1코딩][JS] DOM - 텍스트 노드가 있는 노드 생성 (0) | 2022.08.13 |
| [1일1코딩][Java] Collection : List (0) | 2022.08.12 |